Peter Blum, October 2022 (another update)
Purpose of stratigraphic correlation on the JOIDES Resolution
Shipboard (during expedition)
- Minimize coring gaps
- Provide rapid correlations when drilling multiple holes (starting with the top cores of hole B) to ensure coring gaps in existing holes are covered by core in the newest hole.
- Use of the secondary core logger (Special task multisensor logger, STMSL) in addition to the primary logger (whole-round multi-sensor logger, WRMSL) for "out of sequence" rapid logging of selected sections is highly recommended.
- This tasks requires effective real-time communication with the "core tech" from the drilling crew to achieve immediate drilling depth corrections when needed to mitigate coring gaps.
- Construct core composite depth scale below seafloor (CCSF)
- Provide a first order correlation of all cores from multiple holes by depth shifting (affine translation without scaling).
- Shifts can be accomplished by multiple methods, the primary method being a tie point between a reference core and a shifting core (more on that later).
- Make the CCSF scale available to the entire science team via the LIMS database.
- Construct sampling splice
- Provide a primary spliced section, consisting of core intervals from multiple holes.
- The primary splice shall represents as much as possible of the stratigraphic section at a drill site, using the best-quality core intervals.
- Sample locations in the curated core at the core depth below seafloor, method A (CSF-A) depth scale can be mapped easily to the splice using the core offsets that define the CCSF depth scale.
Typically on shore (post-expedition - optional)
- Map non-splice intervals into the the primary splice (includes stretching and squeezing).
- Scale the CCSF depth scale, and/or a modified/mapped variant of it, to other depth scale(s) to match the drillers depth below seafloor (DSF) scale or a wireline logging depth scale.
- Astronomical tuning of the final depth scale.
Workflow and tools
- The workflow for the correlation of stratigraphic records obtained from scientific ocean drilling cores requires multiple applications.
- The workflow summarized here is primarily for the shipboard tasks. However, most of it can be done on shore before and/or after an expedition.
Table 1. Tasks and tools for stratigraphic correlation on and off the JOIDES Resolution.
| Workflow | Data types | Tool on JR | Applicable on shore? | User guide |
|---|
| Prepare data for correlation | Non-image data | Correlation Downloader | Not a this time. Use already prepared data or ask JRSO staff for help. |
|
| Image data | LORE (LIMS Online Reports) | Yes |
|
| ImageResample (R script) | Yes |
|
| Correlate: shift cores and splice core segments | All non-image and image data | Correlator app | Yes |
|
| Load shift offsets and splice interval data to the LIMS database | Affine tables Splice interval tables | SCORS Uploader and Manager | Yes but requires credentials to write to the LIMS database (and approval by project manager) |
|
| Download data with CCSF (core composite depth below seafloor) depths | All data accessible from the LIMS database | LORE (LIMS Online Reports) | Yes |
|
Figure 1-1. Stratigraphic correlation support (SCORS) workflow and tools.
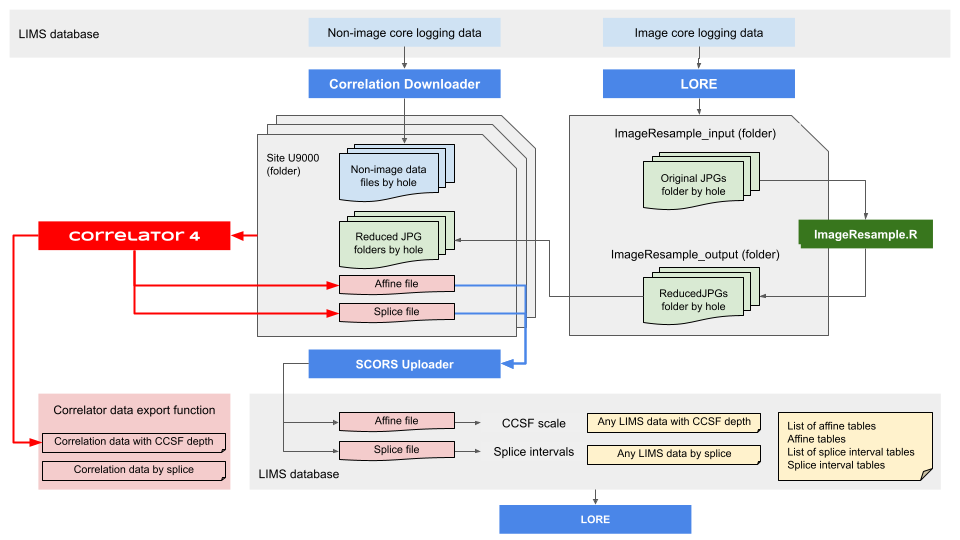
Correlation Downloader (get non-image data)
For a detailed guide, refer to the Correlation Downloader user guide.
In a nutshell, to download core logging data (excluding images) from the LIMS database:
- Open the Correlation Downloader app (ask your friendly IT support if the shortcut is not readily available)
- Select the data types you want to use in Correlator.
- Note the checkbox Split by instrument, it applies mainly or exclusively to magnetic susceptibility data acquired on two loggers and the case where you want to correlate them to each other. Check it to be save. Details in the full user guide.
- Select the hole and core(s) you want the data from (one hole at a time).
- Note: the relevant section summary required for accurate computations in Correlator is downloaded automatically with the first data type you are downloading.
- Note: Check the Append core data to hole button for iterative addition of data from recently recovered core to the hole file.
- Click the Download correlation data button.
- Select your site folder from which Correlator will import the data.
LORE (get image data)
LORE is the main data portal of the JRSO. To batch-download section half images for use in Correlator:
- Go to the LORE page at
- In the report selection panel on the left, select Images > Core Sections (LSIMG) >Standard.
- In the Hierarchy Search panel, select one of the Site(s) and one of the Hole(s).
- Click the View data button.
- Click the Batch download linked files button.
- Select the Cropped image (JPG) link radio button.
- Click the Choose a link button.
- A zip file with all the images will be written to whatever download folder your workstation has configured.
- Go to your Downloads folder and (depending on your OS/browser configuration) either unzip the image file and drag it, or unzip directly it into the the test folder named for the hole and used by the R script, such as:.
- Desktop > Image reduction for Correlator > ImageResample_input > U1510A (or whatever your directory and hole name are)
- This is the currently configured path on the Windows machine at the JR correlation station. You can use whatever directory structure you like, but you have to change the path in the R script accordingly and precisely.
ImageResample
This is the part where you prepare the section half images downloaded from the LIMS database for use in Correlator. This involves cropping the peripheral ~1 cm from the images and reducing the image to ~200 kb. Refer to the Image reduction for Correlator user guide for details. In a nutshell, to batch-process the images:
- Confirm that the images you want to reduce are in the input folder:
- Desktop > Image reduction for Correlator > ImageResample_input > U1510A (or whatever your directory and hole name are)
- Open R. If it's not installed, ask your friendly IT support person. Mention that the library (package) "magick" needs to be installed too.
- Go to File > Open script, navigate to the ImageResample.R file, and open it (or whatever other method you use to open the file).
- Important: Add the test (hole) folder name to the script, comment out or delete other test names.
- Use Select all of the script and click Ctr-R to run it.
- Lean back and watch the process in the Console window - be patient, a progress bar may not appear.
- When the End of script line appears, check the ImageResample_output > U1510A (or whatever your hole name is) folder to confirm the reduced image files.
- Drag the U1510A (or whatever your hole name is) folder into the site data folder used by Correlator to import data, e.g.:
- Desktop > Data from LIMS for Correlator > Site U1510 (or whatever site you are working on).
Correlator
This is the main, big and fancy, feature-rich application that allows you to correlate core data from multiple holes at a drill site, by
- depth shifting cores using high-resolution core logging data to construct a core composite depth below sea floor (CCSF) depth scale;
- splicing selected core intervals to construct the most complete stratigraphic representation possible at a site.
This is a Python application that is installed locally:
- The JR correlation station should have it installed, else JRSO personnel can point you to the person who can help.
- A Google drive repository is currently maintained for use on shore, including all the resources used on the JR.
- The contract developer also has a GItHub site where you should be able to find the latest version of Correlator:
SCORS Uploader and Manager
Load affine tables and splice interval tables created by an external application (e.g., Correlator) to the LIMS database where the information can be reported and applied to all data in LIMS.
LORE again (get correlated data)
Provide (A) lists of existing affine tables and splice interval tables, with links to uploaded user files; (B) detailed, LIMS-computed affine and splice interval tables; (C) CCSF (alternate) depths for any data set in the LIMS; and (D) data sets by selected splice.
